Slides: 4 - Multi-attribute Decision Analysis.pdf
ArcGIS magic
Switching to RD New coordinate system:
- Right click map → properties
- Go to projected coordinates → Europe → RD New
MADA methods:
- Weighted Linear Combination
- Analytic Hierarchy Process
- Ideal Point Methods
Weighted Linear Combination
Where is the overall value of the i-th alternative at location, 𝑠𝑖 , defined by the (𝑥𝑖, 𝑦𝑖) coordinates
And is value of the ith alternative with respect to the k-th attribute measured by means of the value function
Proximity-adjusted WLC
Based on the idea of adjusting preferences according to the spatial relationship between alternatives, or an alternative and some reference locations
Local WLC
Compares only to neighbors, so gives a relative scale
(Copy from slides)
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
One of the most comprehensive methods of MCDA
Based on three principles:
- Decomposition
- requires that a decision problem be decomposed into a hierarchy that captures the essential elements of the problem
- Comparative judgement
- requires assessment of pairwise comparisons of the elements within a given level of the hierarchical structure, with respect to their parent in the next-higher level
- Synthesis of priorities
- takes each of the derived ratio scale priorities in the various levels of the hierarchy and constructs a composite set of priorities for the elements at the lowest level of the hierarchy (that is, alternatives)
Involves three main steps:
- Developing the AHP hierarchy
- Assigning weights of importance to each element of the hierarchical structure
- Using the pairwise comparison method
- Constructing an overall priority rating
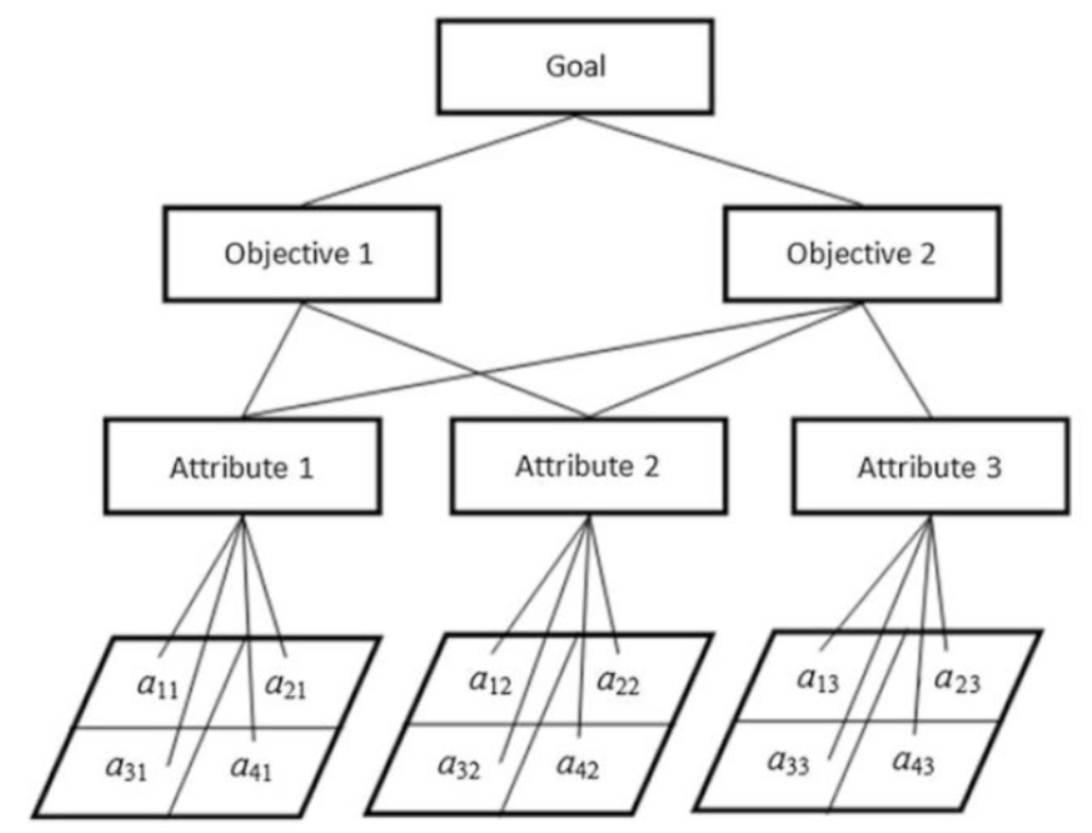
Note
An attribute can affect more than one objective!
These relationships could be both positive and negative, i.e. an attribute may affect objective 1 positively, while affecting objective 2 negatively.
This means that in a comparison matrix, attributes have a weight value for each objective.
Ideal point methods
Based on evaluating decision alternatives with reference to some specific target or goal (try to minimize/maximize the separation)
Reference point: any significant target or goal against which the decision alternatives are evaluated
This hypothetical alternative is often defined in terms of the positive ideal (utopia) point, or negative ideal (or anti-ideal or nadir) point
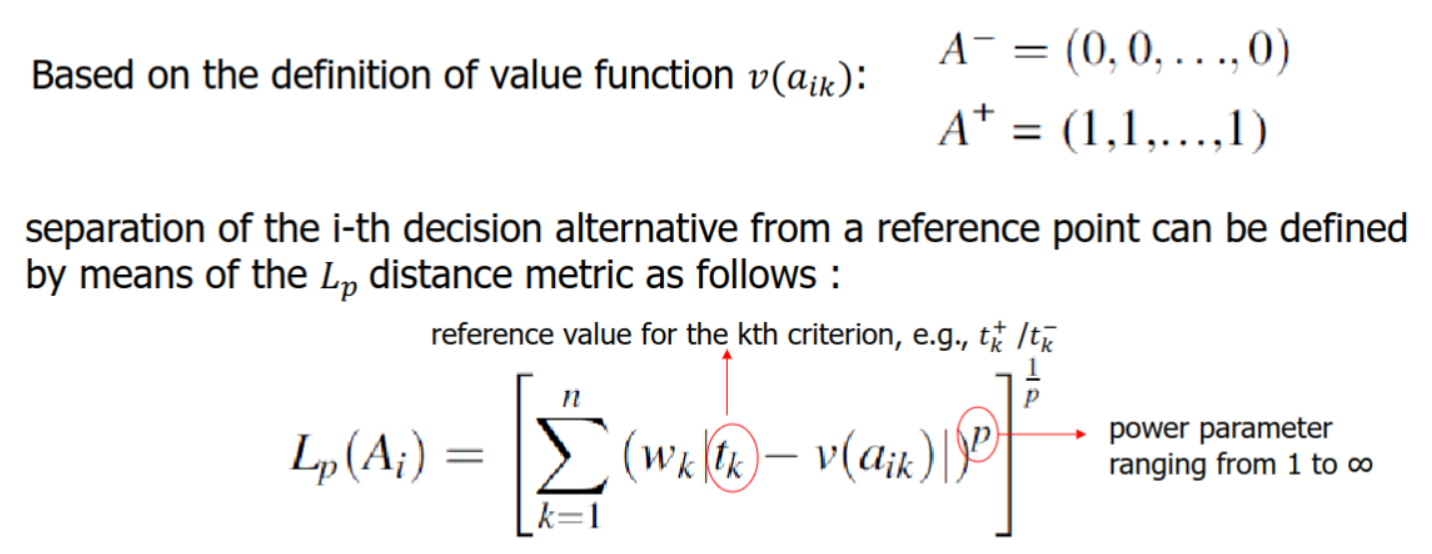
^ Calculates the absolute distance between and the reference point
Distance metrics
So far we have been using the Manhattan (rectangular) distance between two points, also denoted as .
Instead, we can also use the Euclidean distance:
TODO
- Assignment 2
- Read reference book